

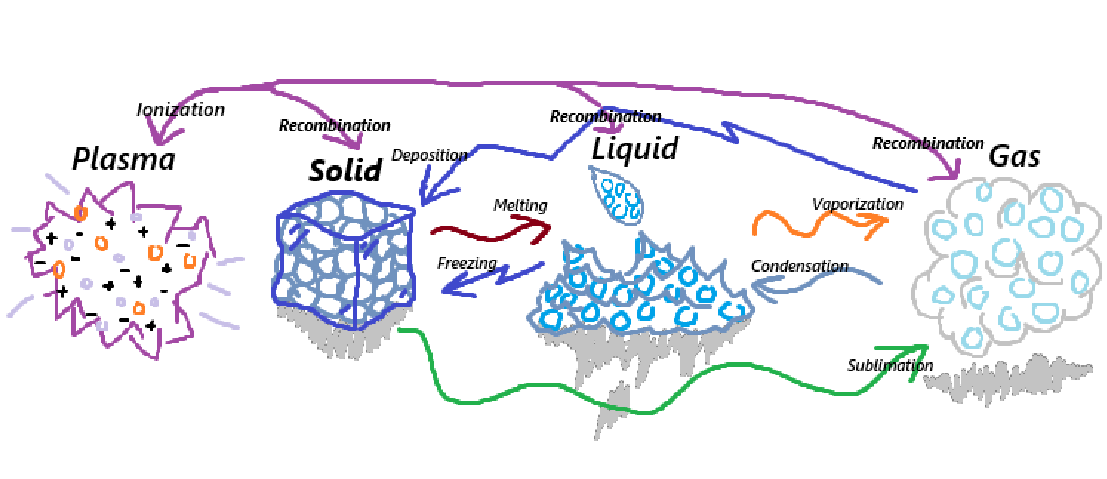
Solids can go through the process of being melted into a Liquid
Solids can go through the process of sublimation into a Gas
Solids can go through the process of ionization into a Plasma
Liquids can go through the process of Freezing into a solid
Liquids can go through the process of Vaporization into a Gas
Liquids can go through the process of Ionization into a Plasma
Gasses can go through the process of Sublimation into a Solid
Gasses can go through the process of Condensation into a Liquid
Gasses can go through the process of Ionization into a Plasma
Plasma can go through the process of Recombination into a Gas
Plasma can go through the process of Recombination into a Liquid
Plasma can go through the process of Recombination into a Solid
Melting occurs when solids are heated enough that the particles gain enough energy to overcome fixed positions, losing its compression in the process.
Sublimation is the result of when a solid turns into a gas without turning into a liquid or going through the state of being a liquid.
Ionization is when any phase of matter can be turned into plasma, through extreme temperatures, this is typically the result of electrons being removed from atoms.
Vaproization is when a liquid absorbs enough heat for the molecules to begin spreading out which forms a gas, as this typically occurs during boiling.
Condesation is when a gas loses its heat and the particles slow down enough that it compresses causing the molecules to form a liquid.
Deposition occurs whenever a gas goes directly to a solid whilst avoiding the liquid phase, as this occurs when gas molecules lose enough energy. Like water vapor freezing directly into solid ice crystals.